In the realm of health, fatty liver disease has emerged as a significant concern, characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver tissue, hindering its natural functions. Even in its early stages, prompt and proactive treatment is essential to prevent potential complications. Delve into the following article to gain a deeper understanding of fatty liver disease, its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures.
1. What is Fatty Liver Disease, and How Does it Progress?
In a healthy individual, the liver contains a moderate amount of fat, ranging from 3% to 5% of its total weight. This is considered a safe threshold for optimal health. Once the fat content exceeds 5%, the individual is diagnosed with fatty liver disease.
As the fat accumulation in the liver increases, the organ’s functionality significantly diminishes, adversely impacting overall health. Initially perceived as a benign condition, fatty liver disease can progress and lead to severe complications, including liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, and even life-threatening liver cancer.
Presently, the disease is categorized into three main stages, each exhibiting varying degrees of fat accumulation, symptoms, and levels of risk.
– Stage 1: Fat accumulation ranges from 5% to 10%, posing minimal harm to the liver.
– Stage 2: Fat comprises 10% to 25% of the total liver weight.
– Stage 3: Fat surpasses 30%, marking the most hazardous stage.
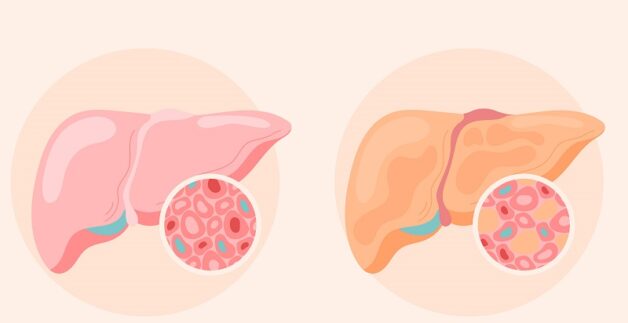
Fatty liver is categorized into three main stages
2. Recognizing Fatty Liver Symptoms
Early stages may manifest subtly, with symptoms like fatigue and mild abdominal discomfort. Pronounced signs emerge as fat increases, including abdominal swelling, red palms, digestive bleeding, and jaundice. Detection often occurs during routine check-ups or ultrasounds, underlining the disease’s elusive nature.
Early stages may manifest subtly, with symptoms like fatigue and mild abdominal discomfort.
3. Decoding Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
3.1 Alcohol-Related Causes
Chronic alcohol consumption ranks among the primary triggers, hindering effective fat metabolism. Risk factors include obesity, malnutrition, viral hepatitis, age, and genetics. Persistent alcohol intake accelerates disease progression.
3.2 Non-Alcohol-Related Causes
Diverse factors contribute, such as:
– Obesity: Direct correlation between body weight and liver fat.
– Malnutrition: Essential nutrient deficiency impairs apolipoprotein synthesis, leading to triglyceride buildup.
– Rapid Weight Loss: Stress on the liver during abrupt weight loss.
– Diabetes: Insulin-related metabolic disruptions elevate fatty liver risk.
– Medication Side Effects: Prolonged unprescribed medication use may interfere with liver functions.
4. Treatment Considerations for Fatty Liver Patients
Fatty liver often advances discreetly, demanding vigilance. Despite the lack of a specific cure, patients are advised to:
– Embrace a healthier lifestyle.
– Adopt a balanced and nutritious diet.
– Abstain from alcohol consumption.
– Engage in regular and enhanced physical activity.
– Effectively manage underlying health conditions.
Fatty liver disease warrants proactive attention due to its elusive nature and potential ramifications. While a definitive cure remains elusive, lifestyle modifications, abstinence from alcohol, and diligent health management play pivotal roles in mitigating symptoms and preventing disease escalation. Recognizing fatty liver disease as more than a benign condition emphasizes the importance of active patient engagement and timely medical intervention.