Cervical disc herniation, traditionally associated with older individuals, is increasingly being diagnosed in younger people. This condition can lead to significant complications and severely impact the quality of life. But why are more young people experiencing cervical disc herniation, and what are the treatment options? This article will explore the key aspects of cervical disc herniation in young adults.
1. What is Cervical Disc Herniation?
1.1. Understanding the Cervical Disc
The cervical disc acts as a cushion between the vertebrae in the neck. Shaped like a flat, round capsule, these discs help connect the vertebrae, distribute mechanical loads, and protect the spine. Each disc consists of two main parts:
– Nucleus Pulposus: This is a soft, jelly-like center that provides the disc with its elasticity.
– Annulus Fibrosus: Surrounding the nucleus, the annulus fibrosus is an elliptical membrane made up of collagen fibers. It serves to protect the nucleus and maintain the structural integrity of the cervical spine.
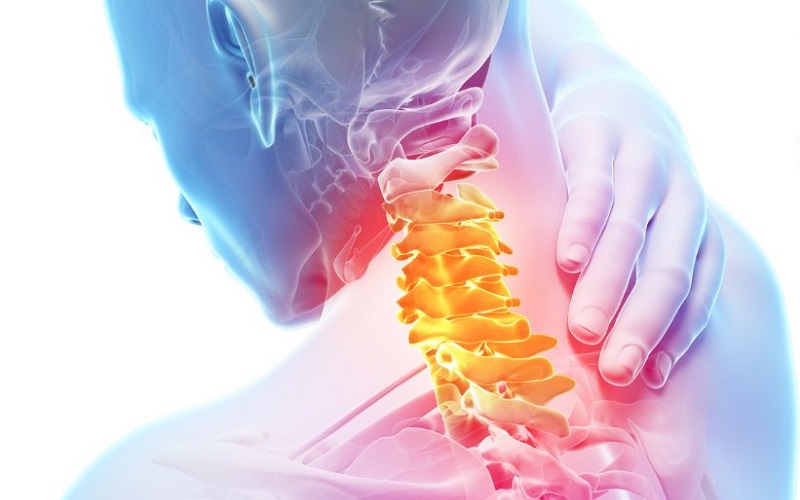
The disc is a cushion between cervical vertebrae that connects them and absorbs impact.
1.2. Cervical Disc Herniation
Cervical disc herniation occurs when the nucleus pulposus escapes through a tear in the annulus fibrosus, compressing the spinal cord or nerve roots. This can lead to symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and inflammation in the neck area. If left untreated, it may result in severe complications.
2. Causes of Cervical Disc Herniation in Young Adults
Several factors contribute to the increasing incidence of cervical disc herniation among young people:
2.1. Poor Posture Over Time
Long-term poor posture, such as sitting with a tilted head or slouching, significantly increases the risk of cervical spine conditions, including disc herniation. Young people, especially those who spend extended periods sitting in front of computers or looking down at their phones, are particularly vulnerable. Additionally, heavy physical labor, such as lifting or construction work, can put undue stress on the spine, leading to cervical disc herniation in young adults.
2.2. Sudden Injuries
Traumatic events, such as car accidents or sports injuries, often impact muscles, bones, and joints, putting pressure on the cervical discs. High-intensity activities, especially without proper conditioning and preparation, can also lead to disc herniation.
2.3. Obesity
Obesity is a significant risk factor for cervical disc herniation in young adults. Unhealthy habits like late-night eating, excessive consumption of carbohydrate-rich foods, and lack of exercise can lead to rapid weight gain. Increased body weight places additional pressure on the joints, particularly in the neck, heightening the risk of cervical disc herniation in young adults.

Obesity is one of the causes of cervical disc herniation.
2.4. Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices
Harmful habits, such as smoking, physical inactivity, and poor nutrition, can weaken disc health. Specifically:
– Smoking reduces the oxygen supply to the discs, accelerating degeneration.
– Lack of physical activity weakens the muscles surrounding the discs, reducing their ability to support the spine.
– Poor nutrition deprives the discs of essential nutrients necessary for maintaining their health.
Avoiding these habits and adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of cervical disc herniation in young adults.
3. Effective Treatment Methods
Treatment for cervical disc herniation in young adults depends on the severity and location of the herniation, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
3.1. Medication
For mild cases, medication can help reduce pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and nerve pain relievers are often prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
3.2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy aims to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, reduce pain, and enhance mobility. Techniques like ultrasound therapy, massage, and spinal traction are commonly used. It’s crucial to perform these exercises under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid further injury.
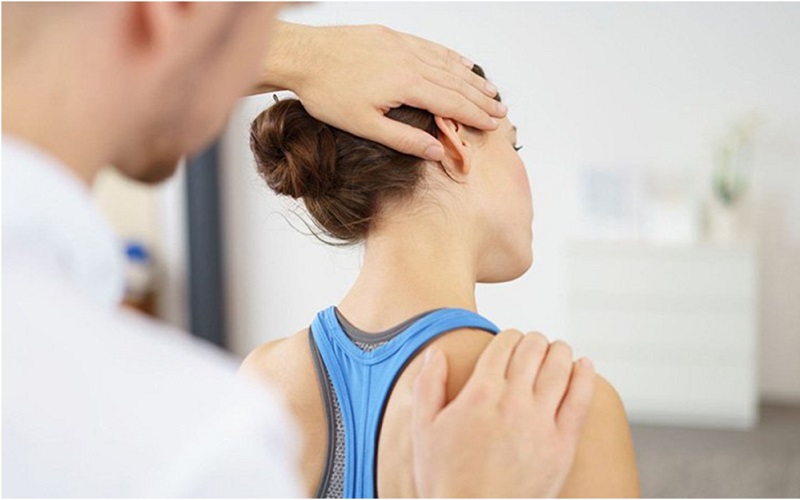
Physical therapy helps alleviate pain caused by the condition.
3.3. Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the herniated portion of the disc and stabilize the spine using artificial discs or bone grafts.
Throughout treatment, patients should follow their doctor’s recommendations, avoid activities that put pressure on the cervical spine, and maintain a healthy diet to promote recovery.
Cervical disc herniation in young adults is a growing concern and can lead to serious complications if not addressed promptly. Early detection and treatment are essential for preventing further damage and ensuring a quick recovery. Taking steps to protect spinal health and prevent the onset of this condition is vital for maintaining a high quality of life.








