Tonsillitis is a common condition, especially during seasonal transitions when the body becomes more vulnerable to bacterial and viral infections. The disease not only causes throat pain and difficulty swallowing but can also lead to severe complications if not treated properly. Choosing the right treatment method helps effectively manage the condition and prevent complications, ensuring long-term health. Let’s explore the details of tonsillitis treatment methods and key considerations with TCI.
1. What is Tonsillitis?
The tonsils are part of the Waldeyer’s ring, playing a crucial role in the immune system. These two lymphoid tissue masses, located at the back of the throat, act as the body’s first line of defense against bacteria and viruses entering through the respiratory tract. However, due to frequent exposure to pathogens, the tonsils can become infected, leading to tonsillitis.
When inflamed, the tonsils swell, turn red, and may develop white pus spots on their surface. The primary causes are bacterial or viral infections, particularly Group A Streptococcus. Factors such as weather changes and a weakened immune system also contribute to an increased risk of the disease.
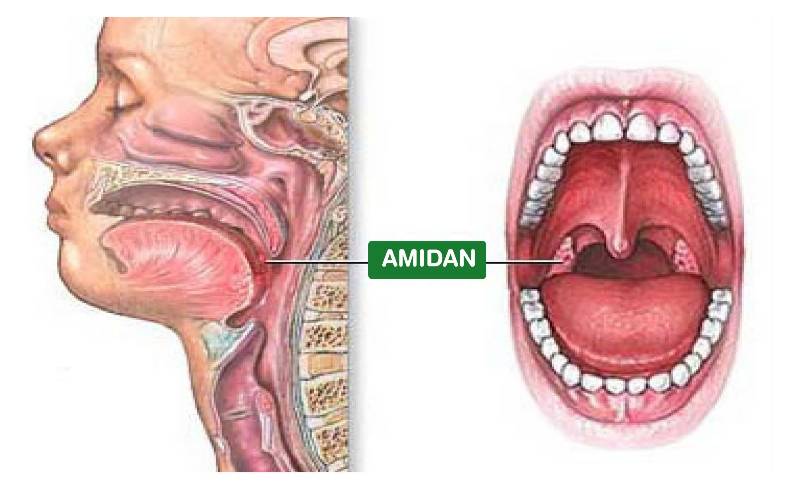
Illustrative image of the tonsil location
Tonsillitis is classified into acute and chronic types based on the duration and recurrence of symptoms. Acute tonsillitis typically lasts from a few days to two weeks, while chronic tonsillitis can persist for months or even years with intermittent flare-ups.
1.1. Acute Tonsillitis
This condition occurs suddenly, usually due to viral or bacterial infections. Symptoms include a sore throat, high fever, difficulty swallowing, swollen red tonsils, and sometimes white pus deposits.
1.2. Chronic Tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by persistent or frequently recurring infections throughout the year. Patients may experience bad breath, persistent throat discomfort, a sensation of obstruction when swallowing, and frequent throat infections.
2. Treatment Methods
Depending on the severity of inflammation and the underlying cause, doctors may recommend medical treatment or tonsillectomy.
2.1. Medical Treatment for Tonsillitis
For acute tonsillitis or chronic tonsillitis without severe complications, treatment focuses on symptom management and eliminating the causative agent. Doctors typically prescribe appropriate antibiotics combined with pain relievers and fever reducers. The choice of antibiotics is based on bacterial culture results and antibiotic resistance assessment.
Examination and use of medication for tonsillitis as prescribed by the doctor
2.1.1. Antibiotic Therapy
If tonsillitis is caused by bacterial infections, appropriate antibiotics will be prescribed to control the infection. Proper use of antibiotics as directed by a doctor is essential to prevent antibiotic resistance.
2.1.2. Pain Relievers and Fever Reducers
Medications such as paracetamol or ibuprofen help alleviate throat pain, reduce fever, and improve patient comfort.
2.1.3. Antiseptic Mouthwashes and Throat Sprays
Mouthwashes containing antiseptic agents help reduce inflammation, eliminate bacteria, and support effective treatment of tonsillitis.
In addition to medication, patients should stay hydrated, get adequate rest, and avoid exposure to pollutants to speed up recovery.
2.2. Tonsillectomy
In cases of recurrent chronic tonsillitis or excessively enlarged tonsils causing breathing difficulties or sleep apnea, a tonsillectomy may be recommended. This surgical procedure is carefully considered based on the patient’s age, health status, and the impact of the disease on daily life.
2.2.1. When is Tonsillectomy Necessary?
– Frequent recurrence of tonsillitis, occurring 5-7 times per year.
– Complications such as joint inflammation, glomerulonephritis, or heart disease.
– Snoring and sleep apnea due to enlarged tonsils.
– Chronic tonsillitis significantly affecting quality of life.
2.2.2. Modern Tonsillectomy Techniques
Various modern tonsillectomy techniques minimize pain and reduce recovery time, including electrocautery, laser surgery, and plasma knife surgery. Hospitals such as Thu Cuc TCI and other major medical institutions commonly use Coblation technology with Plasma, which minimizes tissue damage, reduces pain, and shortens recovery time, making it suitable for patients of different ages.
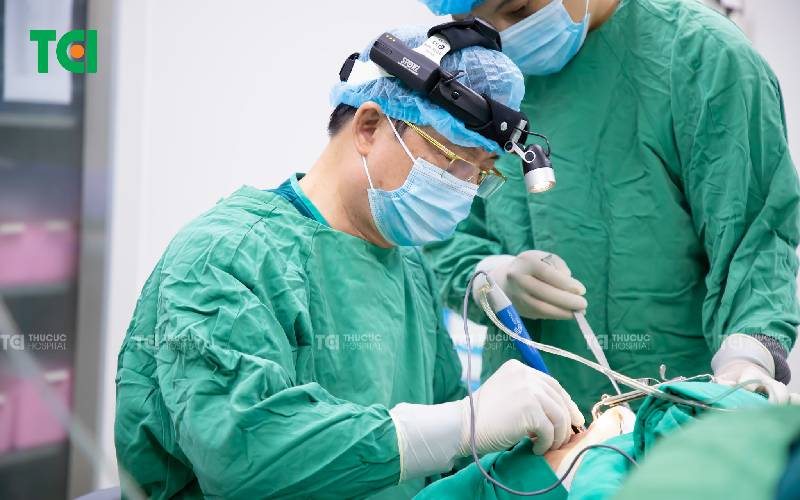
Tonsillectomy using the modern Plasma Coblation technique at TCI
3. Important Considerations for Tonsillitis Treatment
Regardless of the chosen treatment method, patients should follow these essential guidelines to ensure effective recovery:
3.1. Post-Treatment Nutrition for Patients
A well-balanced diet is crucial for recovery. Patients should increase their intake of vitamin C-rich and antioxidant-rich foods to boost immunity. Soft, easy-to-swallow foods are recommended, while spicy and irritating foods should be avoided.
3.2. Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a clean and well-ventilated living environment, avoiding irritants such as smoke and dust, and practicing proper oral hygiene are essential. Ensuring sufficient and quality sleep also helps strengthen the immune system.
4. Monitoring and Preventing Complications
4.1. Warning Signs to Monitor
During treatment, patients should be aware of warning signs such as high fever, breathing difficulties, persistent swallowing problems, or severe throat pain. If symptoms do not improve or worsen, immediate medical attention is necessary.
4.2. Preventing Recurrence
After successful treatment, preventive measures should be taken to avoid recurrence. These include avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and attending regular medical check-ups as advised by a doctor.
Tonsillitis is a common yet manageable condition if detected early and treated appropriately. Adhering to medical treatment plans and proper health care routines helps patients recover quickly and prevent serious complications. To ensure the best treatment outcomes, patients should choose reputable medical institutions with experienced specialists and modern equipment. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle and following preventive measures will minimize the risk of tonsillitis and its recurrence.








