Vestibular disorders are common health conditions that significantly impact the quality of life. Understanding these disorders not only helps improve symptoms but also prevents potential complications effectively.
1. What Are Vestibular Disorders?
1.1. The Vestibular System and Its Role in the Body
The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and spatial orientation. When this system is impaired, individuals may experience dizziness, loss of balance, and nausea.
1.2. Definition of Vestibular Disorders
Vestibular disorders refer to dysfunctions of the vestibular system, resulting in symptoms such as vertigo, dizziness, and balance disturbances. Rather than being a single disease, these disorders are often indicative of various underlying health issues, ranging from stress and sleep deprivation to more severe conditions such as inner ear infections or neurological disorders.
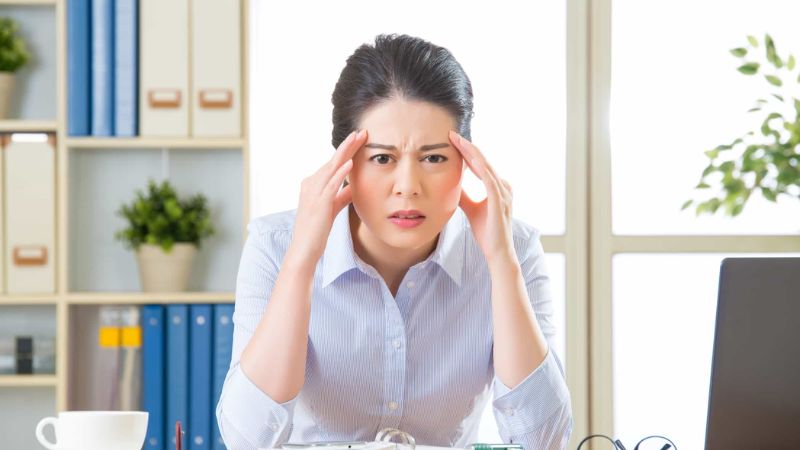

Vestibular system abnormalities may cause dizziness, vertigo, and headaches.
2. Causes and Risk Factors of Vestibular Dysfunction
2.1. Underlying Medical Conditions
The most common causes of vestibular dysfunction include inner ear conditions such as labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis. Additionally, chronic stress and unhealthy lifestyle habits can contribute to the onset of these disorders.
2.2. Environmental and Age-Related Factors
Aging increases the risk of vestibular disorders, particularly among the elderly. Environmental factors such as exposure to pollution, loud noises, and sudden changes in air pressure can also negatively affect the vestibular system.
3. Symptoms of Vestibular Disorders
3.1. Early Warning Signs
The most prevalent symptom of vestibular dysfunction is dizziness or a sensation of spinning. Patients often feel as though their surroundings are moving uncontrollably, accompanied by nausea and fatigue.
3.2. Severe Symptoms Requiring Medical Attention
In more serious cases, individuals may struggle to maintain posture, experience frequent falls, and suffer from persistent dizziness. If left untreated, these symptoms can lead to dangerous complications and long-term health consequences.
4. How to Manage and Prevent Vestibular Disorders
4.1. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
A balanced lifestyle is essential for preventing and managing vestibular disorders. Ensuring adequate sleep, maintaining a nutritious diet, and avoiding stimulants such as alcohol and tobacco can significantly reduce symptoms.
4.2. Vestibular Rehabilitation Exercises
Regular physical activity can enhance vestibular function. Exercises such as yoga, tai chi, and simple balance training routines are effective in improving coordination and reducing dizziness.
4.3. Medical Treatments
For severe cases, seeking professional medical assistance is necessary. Depending on the cause, treatment may involve medication or medical interventions. However, all treatments should be administered under the guidance of a healthcare specialist.
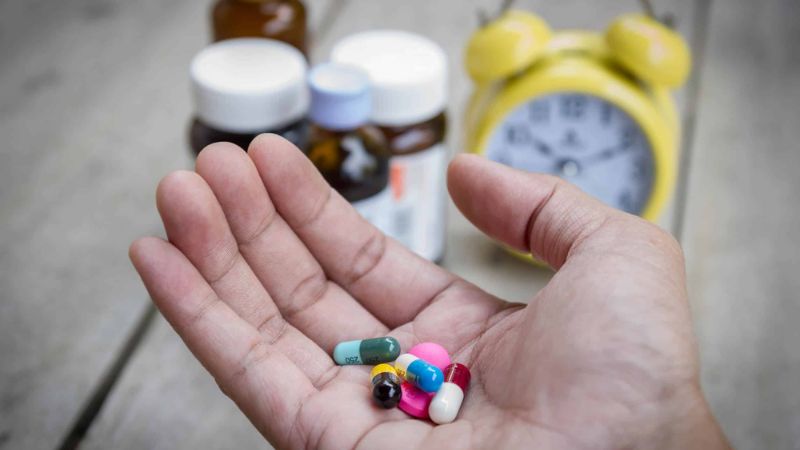

Certain medications can help improve vestibular dysfunction.
5. Common Misconceptions About Vestibular Disorders
5.1. Are Vestibular Disorders Harmless?
Many people assume that vestibular disorders are minor and do not require medical attention. However, if not properly managed, they can severely impact overall health and daily activities.
5.2. Are Vestibular Disorders Exclusive to the Elderly?
While older adults are at higher risk,vestibular dysfunction can affect individuals of all ages. Those working in high-stress environments or leading sedentary lifestyles are also vulnerable.
6. Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches for Vestibular Disorders
Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing vestibular disorders, as they help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Timely diagnosis significantly improves recovery time and overall well-being.
6.1. Recognizing Vestibular Disorders Early
Early diagnosis is key to controlling and treating vestibular conditions effectively. Common symptoms include:
– Vertigo and dizziness
– Nausea and vomiting
– Fatigue and weakness
– Difficulty concentrating, leading to reduced productivity
If you experience these symptoms, consulting a specialist for proper evaluation and treatment is recommended. In cases of sudden or severe symptoms, such as dizziness accompanied by loss of consciousness or breathing difficulties, immediate medical attention is necessary.
6.2. Diagnostic Methods for Vestibular Disorders
To accurately diagnose vestibular disorders and determine their severity, physicians may use various methods, including:
– Clinical Examination: A series of neurological and balance tests to assess vestibular function.
– Blood Tests and Ultrasound: These help rule out other conditions, such as anemia, infections, or cardiovascular diseases.
– Vestibular Function Tests (VNG or ENG): Specialized assessments measuring the vestibular system’s response and detecting abnormalities.
– MRI or CT Scans: Used when there is suspicion of serious conditions such as brain tumors or neurological damage.
Consult a neurology specialist at Thu Cuc TCI if you experience vestibular dysfunction
6.3. Treatment Options for Vestibular Disorders
Early intervention can minimize symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment strategies depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, including:
– Medications: Anti-vertigo drugs, anti-inflammatory medications, and vestibular support supplements.
– Physical Therapy: Specialized rehabilitation exercises designed to restore balance and coordination, often conducted under professional supervision.
– Surgical Interventions: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary, particularly if the disorder is linked to serious conditions like brain tumors or inner ear damage.
– Lifestyle Modifications:
+ Proper Nutrition: A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium, supports nervous system and vestibular health.
+ Regular Exercise: Engaging in activities like walking, yoga, or tai chi strengthens the vestibular system and overall well-being.
+ Stress Management: Relaxation techniques, including meditation, deep breathing exercises, and massage therapy, help reduce stress levels and improve vestibular function.
Conclusion
Vestibular disorders are not simple health concerns but can be effectively managed and prevented with proper understanding. Being attentive to early symptoms, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking timely medical intervention are key to protecting your overall health and well-being.








