Vaccines are essential for protecting public health, preventing numerous life-threatening diseases, and promoting community immunity. However, some individuals may experience allergic reactions after receiving a vaccine. While most reactions are mild and resolve on their own, rare severe reactions require prompt medical intervention. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and management of vaccine allergies, helping readers better understand and address this uncommon occurrence.
1. Understanding Vaccine Allergies
1.1 What Are Vaccine Allergies?
Vaccines play a critical role in disease prevention, from common illnesses to potentially fatal conditions. However, some people may not tolerate vaccines fully and could develop allergic reactions. These reactions occur when the immune system misidentifies certain components in the vaccine, such as egg proteins, gelatin, or preservatives, as harmful substances.
Allergic reactions to vaccines range in severity:
– Mild reactions include symptoms like pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site, mild fever, or fatigue. These symptoms typically subside within a few days.
– Severe reactions, although rare, may include difficulty breathing, anaphylaxis, seizures, or widespread rash. Such cases require immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
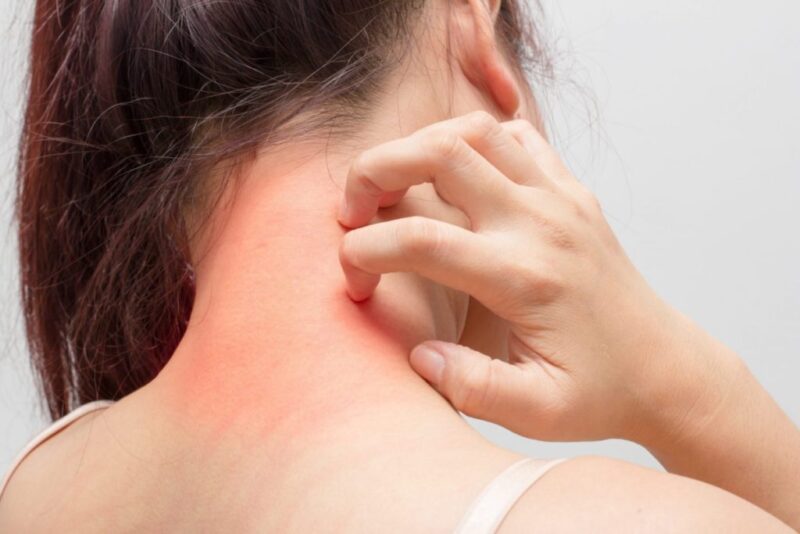
Allergic reactions to vaccines are a possible occurrence after immunization.
1.2 Causes of Vaccine Allergies
The immune system’s response to certain vaccine components is the primary cause of allergic reactions. Individuals with a history of allergies or a genetic predisposition are at higher risk. Common allergens in vaccines include:
Preservatives: Used to ensure vaccine safety.
Egg proteins: Found in some flu and yellow fever vaccines.
Gelatin: A stabilizing agent in certain vaccines.
2. Preventing and Managing Vaccine Allergic Reactions
2.1 Preventing Allergies Before Vaccination
Preventive measures are crucial, especially for individuals at higher risk of allergies. Consider these steps to minimize risks:
– Inform your doctor about your allergy history: Share details about any allergies to foods, medications, or vaccine ingredients like eggs or gelatin.
– Pre-vaccination health check-up: For high-risk individuals, doctors may perform thorough evaluations or conduct test doses to assess tolerance.
– Choose reputable vaccination facilities: Select clinics with experienced medical professionals and proper emergency equipment to ensure safety in case of a reaction.
– Post-vaccination monitoring: Stay at the vaccination site for at least 30 minutes after receiving a vaccine. This allows immediate intervention if a severe reaction occurs.
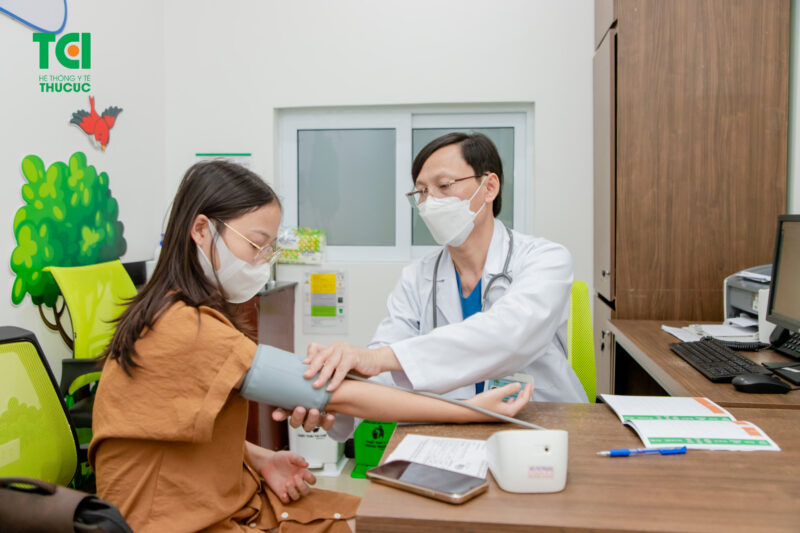

Careful pre-vaccination screening helps prevent post-vaccination reactions.
2.2 Managing Vaccine Allergic Reactions
Mild Reactions:
– Use over-the-counter pain relievers like paracetamol or ibuprofen to alleviate pain and reduce fever.
– Apply a cold compress to the injection site to minimize swelling and discomfort.
– Rest and hydrate as needed. These symptoms typically resolve within a few days.
Severe Reactions:
– Call emergency services immediately if symptoms like difficulty breathing, widespread rash, facial swelling, or anaphylaxis occur.
– Administer epinephrine (adrenaline) if prescribed for anaphylactic emergencies.
– Seek immediate hospitalization for further evaluation and treatment.
3. The Importance of Vaccination
Despite the small risk of allergic reactions, the benefits of vaccination far outweigh potential risks. Vaccines have proven highly effective in preventing severe illnesses such as measles, meningitis, diphtheria, and COVID-19. Thanks to vaccines, global mortality and morbidity rates from these diseases have significantly declined.

Vaccines play a vital role in preventing infectious diseases.
Vaccination not only protects individuals but also fosters herd immunity, reducing the spread of diseases within communities. To ensure safe immunization, discuss your health status and allergy history with a qualified healthcare provider before vaccination.
Vaccine allergies are rare but can occur. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of allergic reactions, individuals can approach vaccination with confidence and preparedness. Choosing reputable vaccination centers and closely monitoring post-vaccination reactions are key to ensuring safety. Vaccination remains one of the most effective ways to protect yourself and your community from dangerous diseases, making it a vital component of public health efforts.








