Sexually transmitted diseases – STDs in men often present with subtle or no symptoms, leading to delays in detection and treatment. These diseases spread rapidly through unsafe sexual activities. Equipping yourself with essential knowledge is crucial to safeguarding your reproductive health and that of your partner.
1. Definition of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections transmitted from one person to another through sexual activities, including vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse. Both men and women can contract STDs, not only through sexual contact but also through transmission from mother to child during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or sharing unsterilized needles.
Annually in Vietnam, over 50,000 individuals seek medical consultation and treatment for sexually transmitted infections at hospitals, but the actual number of infected individuals is estimated to be much higher. Due to stigma, anxiety, and complacency, STDs continue to silently spread in society, affecting future reproductive health.
2. Symptoms of STDs from Unsafe Sexual Activities
The symptoms of STDs in men can appear at any time (initial infection, incubation period) or may be asymptomatic. On average, it takes about 20 days or less for symptoms to manifest in men, depending on the type of disease and individual health.
The signs of STDs are varied and may include:
– Genital sores (e.g., in cases of genital herpes or HPV)
– Urethritis (common with gonorrhea or chlamydia infections)
– Systemic symptoms affecting the whole body (e.g., HIV weakening the immune system)
STDs in men can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites, potentially leading to localized damage or spreading to other organs if not treated promptly. Symptoms are not limited to the genital area and may include fever, rash, blisters in other areas such as the mouth, flu-like symptoms, and fatigue.
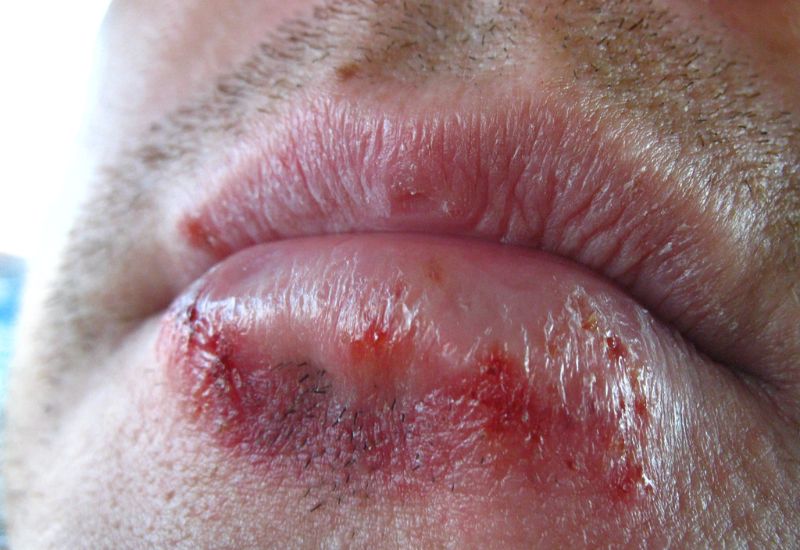
Sexually transmitted diseases often present with subtle symptoms
3. Common STDs in Men
3.1. Genital Warts (HPV)
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of viruses causing sexually transmitted infections in both men and women. Over 200 strains of HPV have been identified, including high-risk types causing cancer and low-risk types causing warts and papillomas. HPV can cause warts on the penis, scrotum, anus, groin, thighs, tongue, and throat. Recurrence is common, with 44% of men experiencing at least one recurrence, and 22% having multiple recurrences. HPV infection can lead to serious complications, including cancer.
3.2. Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection spread through oral, anal, and vaginal sex with an infected person. Common symptoms in infected individuals include painful urination, lower abdominal pain, abnormal discharge from the penis or vagina, pain during intercourse, and testicular pain. Some cases may be asymptomatic. Untreated chlamydia can cause serious complications, such as urethritis, rectal inflammation, and epididymitis.
3.3. Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a prevalent STD that infects the genital, urinary, anal, and throat regions, caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It primarily spreads through unsafe sexual practices, including anal and oral sex. Symptoms in men include difficulty urinating, painful urination, and penile discharge.
3.4. Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a common infection of the genital and urinary tracts caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. It spreads mainly through sexual intercourse, causing vaginal inflammation in women and urethritis in men. In men, the parasite can be found in the urethra, semen, urine, external genitals, prostate, and epididymis. Symptoms may include urethral discharge, painful urination, and urethritis. Complications include epididymitis and prostatitis. Trichomoniasis also increases the risk of HIV infection.
3.5. HIV/AIDS
HIV is a virus that severely weakens the human immune system, progressing to AIDS. Once inside the body, HIV multiplies rapidly and attacks the immune system, making the person vulnerable to other harmful microorganisms. HIV/AIDS is particularly dangerous as it significantly impacts quality of life and can be fatal. Symptoms are often vague and detected late, requiring active treatment to mitigate the virus’s effects.
3.6. Genital Herpes
Genital herpes, also known as herpes simplex virus (HSV), is common among men. Early symptoms are often unnoticed until the disease progresses significantly, making treatment more complex and expensive. Genital herpes can affect quality of life and remains in the body permanently, with treatment focusing on reducing outbreaks.
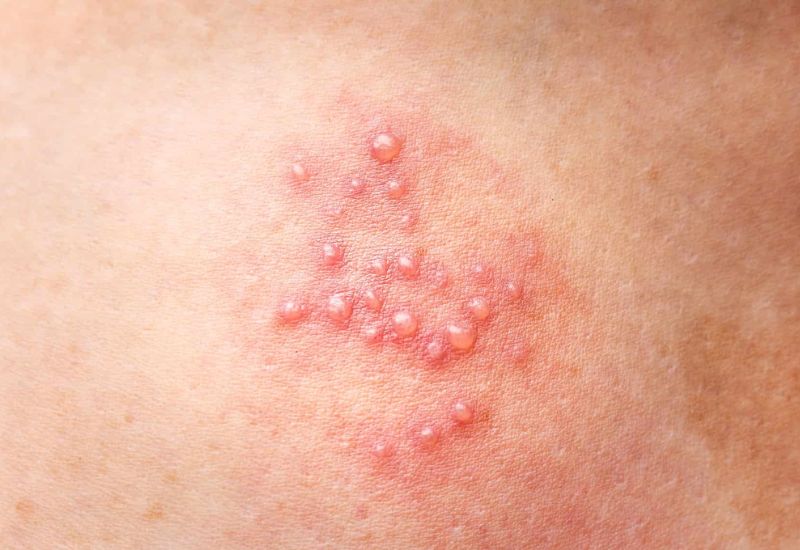
Sexually transmitted diseases are a cause of reduced quality of life and reproductive function in both men and women.
4. High-Risk Groups for STDs in Men
STDs in men can affect individuals of any age, primarily those engaging in unsafe sexual practices or having sex with an infected partner. Despite a large estimated number of infections, only a small fraction seek treatment due to fear of personal information leakage. This hinders efforts to protect and prevent the spread of STDs in society. Men with weakened immune systems or those practicing anal intercourse are at higher risk for these infections.

Men should regularly undergo reproductive health check-ups at reputable medical facilities.
Therefore, the doctors at TCI Thu Cuc Healthcare System recommend regular reproductive health check-ups for men. Frequent examinations help monitor and detect any abnormal signs, allowing for timely and appropriate treatment. Given the complexity of the male reproductive system, regular health check-ups are crucial for preserving reproductive capabilities. Contact us for prompt assistance.








