The seasonal flu vaccine is an effective preventive measure against the impacts of influenza. To help you better understand the importance of flu vaccination, Thu Cuc TCI addresses some frequently asked questions below.
1. Understanding the Severity of Seasonal Influenza
The primary viruses causing seasonal flu belong to the Orthomyxoviridae family and are categorized into three main types: A, B, and C. All three can infect humans, but influenza A is responsible for most large-scale flu outbreaks.
– Influenza A (H1N1, H3N2): These strains have been linked to major flu pandemics and exhibit continuous genetic mutations, leading to new virus variants.
– Influenza B: Though it can cause flu, it does not result in large-scale outbreaks like influenza A and has a more stable genetic structure.
– Influenza C: This type generally causes mild illness and is less common, rarely leading to widespread flu outbreaks.
Seasonal flu primarily spreads through respiratory droplets expelled when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus can rapidly mutate, giving rise to new variants that enhance its transmission potential and epidemic risk.
Fluctuating weather conditions and low humidity levels create favorable environments for flu viruses to infect individuals. Seasonal flu is an acute respiratory illness that can lead to complications such as pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, and other infections if not treated promptly. Severe flu cases may present with high fever, difficulty breathing, pulmonary edema, and in extreme cases, heart failure or even death.
Getting vaccinated against influenza is an effective strategy to reduce the risk of infection and minimize the severity of the disease.

Seasonal flu can lead to pneumonia and respiratory failure if not treated promptly.
2. Is Flu Vaccination Necessary?
Annual flu vaccination offers significant benefits, including reducing the incidence of flu infections, lowering the risk of severe complications, and decreasing hospitalization and mortality rates, especially in children and older adults.
Flu vaccines work by stimulating the body to produce specific antibodies against the influenza virus. These antibodies become effective approximately 2-3 weeks after vaccination, forming a protective immune shield against the virus.
Annual flu vaccination is particularly beneficial for high-risk groups such as older adults and young children. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends yearly flu vaccination for all individuals, including pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Flu vaccination not only reduces the likelihood of infection but also plays a crucial role in protecting communities by limiting virus transmission. Therefore, getting vaccinated annually is an essential step in maintaining public health and preventing flu outbreaks.
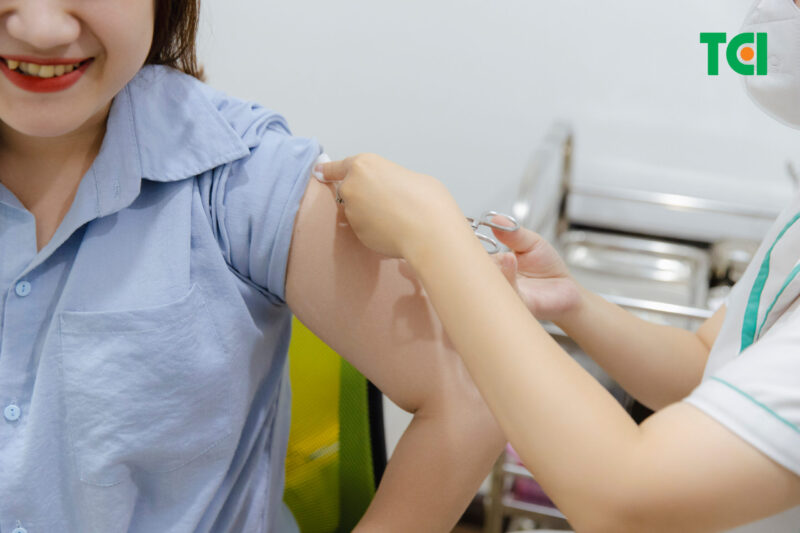
Get an annual flu vaccination to protect against new strains of the influenza virus.
3. Frequently Asked Questions About Flu Prevention
3.1 What Is the Recommended Flu Vaccination Schedule?
To ensure optimal protection, seasonal flu vaccination should be administered annually, particularly due to the emergence of new virus strains. The recommended flu vaccination schedule is as follows:
– Children aged 6 months to under 9 years: Two doses of the flu vaccine, administered one month apart, are required to develop sufficient immunity. A booster shot should be given annually to maintain protection.
– Children 9 months and older and adults: A single dose of the flu vaccine is sufficient, with annual boosters recommended for continued protection.
3.2 Who Cannot Have The Flu Vaccine
While flu vaccination is a highly effective preventive measure, certain individuals should avoid it under specific conditions:
– Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions to flu vaccines or their components.
– Those in poor health or undergoing treatment for serious illnesses.
– Immunocompromised individuals, such as older adults, patients with chronic diseases, or those undergoing immunosuppressive treatments.
Note: It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before receiving a flu vaccine to ensure safety and effectiveness based on individual health conditions.
3.3 When To Get Vaccinated? How Long Does Flu Vaccine Immunity Last?
The flu season typically begins in the fall, peaking between October and March each year. September and October are considered the ideal months for flu vaccination, allowing the immune system to build protection before the peak flu season.
Flu vaccine protection does not last indefinitely. Immunity typically lasts between 6 to 12 months, gradually decreasing over time. However, vaccination remains highly beneficial in preventing flu infection and reducing symptom severity if illness occurs.
3.4 Is Annual Flu Vaccination Necessary?
Annual flu vaccination is crucial for protection against newly emerging flu virus variants. The influenza virus mutates rapidly due to the diversity of genetic segments forming antigenic structures on its surface. This results in hundreds of different flu virus strains, primarily due to genetic recombination between hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) antigenic segments.
The presence of numerous flu virus strains in the community complicates flu prevention and treatment. The World Health Organization (WHO) advises vaccine manufacturers to update flu vaccine formulations yearly to address the most prevalent circulating strains. This ensures that flu vaccines provide effective protection against the latest virus variants, enhancing the overall efficacy of flu immunization programs.
3.5 How Can Seasonal Flu Be Prevented Effectively?
In addition to flu vaccination, adopting the following preventive measures can help reduce the risk of flu infection:
– Frequent handwashing: Washing hands with soap and clean water helps eliminate bacteria and viruses, reducing the likelihood of infection.
– Wearing face masks: Face masks act as a barrier against respiratory pathogens, preventing virus transmission.
– Avoiding touching the face: Refrain from touching the eyes, nose, and mouth with unclean hands to minimize virus exposure.
– Maintaining social distance: Avoid close contact with individuals showing flu symptoms to reduce the risk of transmission.

Maintain a safe distance in environments with a high risk of seasonal flu transmission.
– Healthy diet and nutrition: Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals strengthens the immune system.
– Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity enhances overall health and immune function.
– Limiting exposure to infected individuals: If possible, avoid direct contact with people suffering from flu to minimize infection risk.
We hope this article provides valuable insights into the importance of seasonal flu vaccination. It is essential not to underestimate the risks associated with flu infections. If you have any questions about seasonal flu or flu vaccination, please contact the Thu Cuc TCI Vaccination Center for prompt assistance and guidance.








