High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common yet often silent medical condition. Due to its subtle onset, many individuals overlook the early signs of high blood pressure, increasing the risk of serious complications later. Identifying these signs in specific populations—young adults, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with underlying health conditions is critical for early diagnosis and effective management. This article explores how signs of high blood pressure present differently across various groups, offering insight for timely intervention.
1. Signs of High Blood Pressure in Young Adults
1.1 Often Overlooked Symptoms
In younger individuals, signs of high blood pressure may be mild and easily mistaken for other issues. Occasional dizziness, fatigue after physical activity, or mild headaches at the end of the day are often attributed to stress, overwork, or sleep deprivation. Consequently, many young people delay medical consultation.
Sometimes, hypertension is only diagnosed after a complication has occurred, such as a mild stroke, heart attack, or vision changes due to retinal damage. Symptoms like a rapid heartbeat, facial flushing, or sudden chest discomfort can appear but are rarely linked to elevated blood pressure unless clinically evaluated.
In young adults, symptoms of hypertension are often subtle, such as brief dizziness, fatigue after physical exertion, or mild headaches at the end of the day
1.2 Lifestyle-Related Triggers
Unhealthy habits such as high salt intake, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of exercise, and irregular sleep patterns are major contributors to the development of hypertension in this group. These behaviors can not only increase blood pressure but also mask early warning signs, making detection more difficult.
2. Signs of High Blood Pressure in the Elderly
2.1 Misinterpreted as Normal Aging
Among older adults, signs of high blood pressure often resemble common aging symptoms such as persistent headaches, memory decline, sleep disturbances, or general fatigue. Many perceive these issues as natural aging processes, unaware that they may be caused by elevated blood pressure.
A hallmark symptom is neck pain or stiffness in the morning. Additional signs include tinnitus, blurred vision, and unsteadiness while walking—resulting from reduced cerebral blood flow. These symptoms may appear suddenly or follow a cyclical pattern.
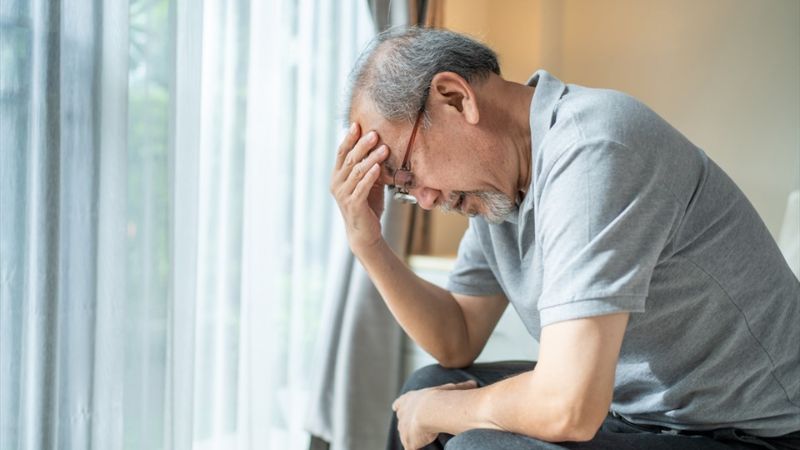

Elderly individuals with hypertension commonly experience chronic headaches, insomnia, and poor balance.
2.2 Greater Risk of Complications
Due to reduced vascular elasticity in older adults, even a minor rise in blood pressure can lead to serious events like stroke or heart failure. Routine blood pressure monitoring and prompt recognition of warning signs are essential to reduce such risks in this age group.
3. Signs of High Blood Pressure in Pregnant Women
3.1 Symptoms of Gestational Hypertension
Pregnancy introduces a unique risk: gestational hypertension, which poses dangers to both mother and fetus. Typical signs of hypertension during pregnancy include swelling in the hands and feet, severe headaches, blurred vision, and visual disturbances like floating spots. Some women may also experience upper abdominal pain or unexplained vomiting.
The presence of protein in the urine (proteinuria) may indicate preeclampsia, a life-threatening complication. Without timely medical intervention, this condition can lead to seizures, organ failure, or maternal death.
3.2 Importance of Regular Monitoring
Detecting signs of high blood pressure during pregnancy should be a top priority. Blood pressure should be assessed at every prenatal visit, along with monitoring weight gain and swelling. Early detection enables effective management through dietary adjustments and safe medications.
4. Signs of High Blood Pressure in Individuals with Chronic Conditions
4.1 Amplified Symptoms in Comorbidities
People with existing conditions like diabetes, dyslipidemia, or heart disease often exhibit more pronounced signs of high blood pressure—such as palpitations, shortness of breath, chest tightness, or limb swelling. Uncontrolled hypertension can exacerbate these conditions, increasing the risk of stroke, heart failure, or myocardial infarction.
In diabetics, damaged nerves and small blood vessels can dull the perception of pain or discomfort, allowing high blood pressure to progress silently.
4.2 Added Treatment Challenges
Managing hypertension in patients with comorbidities is complex and often requires multiple medications and close monitoring. Even persistent mild symptoms like headaches or fatigue could signal poorly controlled blood pressure. These individuals should receive education on symptom recognition and adhere to regular follow-ups.
5. Differentiating Hypertension from Other Conditions
5.1 Common Misdiagnoses
One major challenge in identifying signs of high blood pressure is their overlap with other disorders such as migraines, sinusitis, vestibular disorders, or psychological stress. Symptoms like dizziness and headaches can have different underlying causes.
For instance, hypertension-related headaches typically occur in the back of the head or neck, particularly in the morning or after stress, while headaches from cerebral insufficiency are often accompanied by blurred vision or cognitive fog.
5.2 The Role of Regular Monitoring
The most reliable way to detect high blood pressure is through consistent monitoring. Blood pressure should be measured at the same time daily, during rest, and recorded over time. Early detection allows for timely lifestyle modifications and medical treatment under professional guidance.
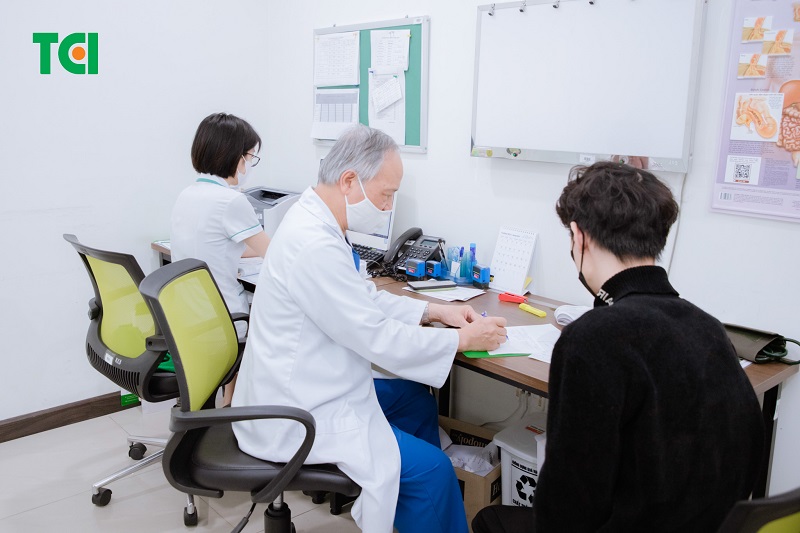

Regardless of age, early medical evaluation is essential when signs of hypertension appear to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
6. Prevention and Management Strategies
6.1 Diet and Physical Activity
A low-sodium diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats is fundamental for blood pressure control. Moderate exercise like walking, swimming, or yoga for 30–45 minutes a day can significantly help maintain normal levels.
6.2 Stress Management and Regular Checkups
Mental stress can trigger spikes in blood pressure, especially in younger individuals and those in high-pressure jobs. Adequate sleep, stress-reduction techniques, and emotional well-being are essential. For those with risk factors such as obesity, smoking, or a family history of hypertension, routine health checkups are crucial for early detection and better treatment outcomes.
In conclusion, signs of high blood pressure vary widely across individuals depending on age, gender, pregnancy status, and underlying health conditions. Early recognition, consistent monitoring, and a proactive lifestyle are key to preventing complications. Don’t wait for a crisis—begin managing your blood pressure today.








