Blood tests are among the most commonly performed diagnostic procedures in modern medicine. For many people, undergoing a blood test is a routine part of a general health check-up. However, few fully understand the scope of information that a blood test can provide and the critical role it plays in detecting various health conditions. This article aims to provide an overview of what blood tests can reveal and the important considerations when undergoing testing.
1. The Purpose of Blood Tests
A blood test is a standard diagnostic tool used in clinical practice. It may be recommended during routine health examinations or ordered to investigate specific symptoms. There are several types of blood tests – some focus on blood cells and platelets, others evaluate substances in the blood such as electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, and proteins. Certain tests also assess mineral levels and immune responses.
The results of a blood test enable doctors to:
– Diagnose diseases or medical conditions.
– Determine the severity or stage of an illness.
– Monitor organ function.
– Guide treatment decisions.
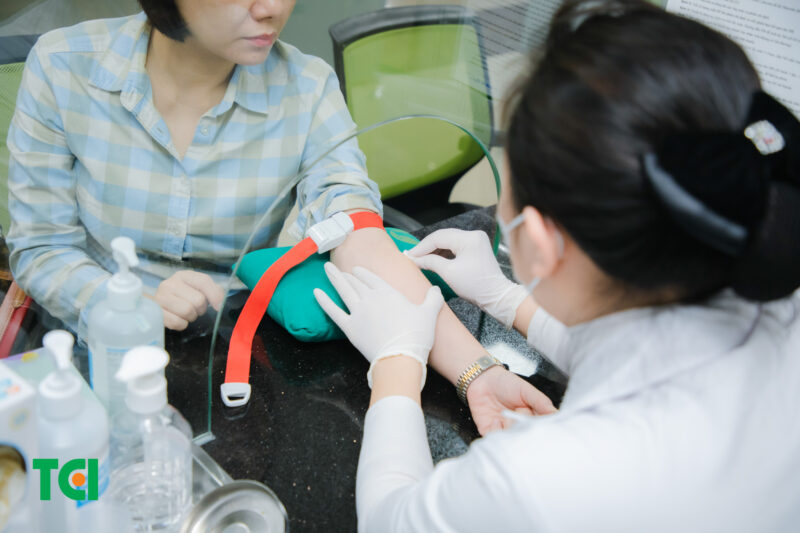
Blood tests are essential diagnostic tools for detecting various medical conditions.
2. Conditions Commonly Detected Through Blood Tests
2.1 Blood Disorders
Any abnormality in the components of blood can indicate a medical issue. A complete blood count (CBC) is a foundational blood test used to detect:
– White blood cell abnormalities – Elevated or decreased levels may indicate infection, immune system disorders, or blood cancers.
– Red blood cell irregularities – Abnormal size or shape may signal anemia, bleeding disorders, or hemolytic anemia.
– Platelet abnormalities – Low or high platelet counts can suggest bleeding disorders or clotting conditions such as thrombosis.
– Hemoglobin levels – Unusual levels may reflect conditions such as thalassemia or sickle cell anemia.
– Hematocrit levels – A low hematocrit indicates anemia, while a high value could point to dehydration.
2.2 Liver and Kidney Function
Elevated creatinine in a blood test can signal kidney issues such as chronic nephritis or renal failure. Liver function tests including ALT, AST, and bilirubin are essential in diagnosing hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. If abnormalities are found, further testing may be needed for confirmation.
2.3 Metabolic and Hormonal Disorders
Blood tests are vital for detecting metabolic imbalances and endocrine issues:
– Diabetes – Elevated blood glucose indicates prediabetes or diabetes, a serious and prevalent chronic condition.
– Lipid disorders – Abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels suggest dyslipidemia.
– Hormonal imbalances – Changes in hormone levels can point to thyroid disorders, adrenal issues, or reproductive hormone disruptions.
Routine blood testing allows early detection and management of these conditions before complications arise.
2.4 Cardiovascular Diseases
Blood tests help assess cardiovascular risk by measuring triglyceride and cholesterol levels. Abnormal results may indicate a higher likelihood of developing coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis, or other heart conditions.
2.5 Infectious Diseases
Blood tests also play a crucial role in identifying infections, including sexually transmitted diseases and viral illnesses. Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, syphilis, hepatitis A/B/C, gonorrhea, and even influenza can be diagnosed through specific blood markers.
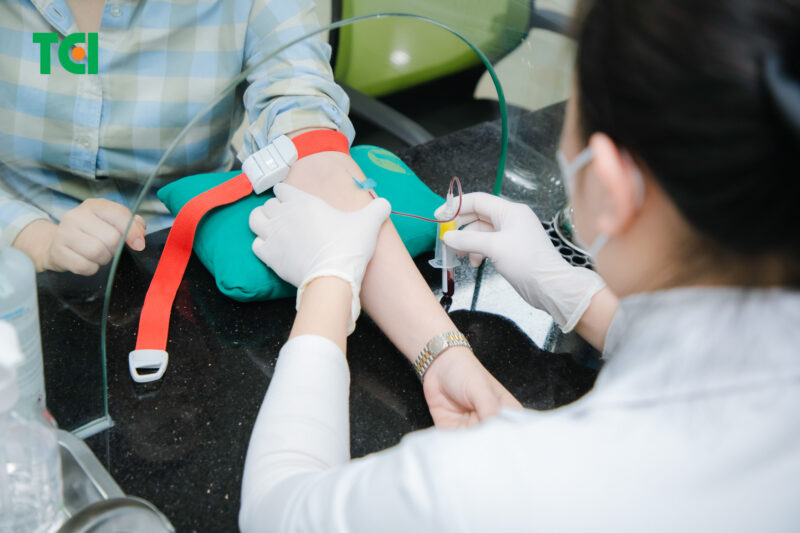
HBV testing supports accurate diagnosis of hepatitis B.
3. Important Precautions Before a Blood Test
To ensure accurate blood test results, patients should observe the following guidelines:
– Fasting: Refrain from eating for 8–10 hours prior to the test. Morning testing is usually recommended.
– Hydration: Water is permitted, but avoid any flavored or sugary beverages, tea, coffee, alcohol, or stimulants.
– Medication disclosure: Patients with chronic conditions or those taking medication should inform their doctor in advance to avoid interference with test outcomes.
– Relaxation: Try to remain calm—blood sampling is generally quick and causes minimal discomfort.

Fasting for at least 6–8 hours is required before a blood test.
4. Where to Get Reliable Blood Tests in Hanoi
In Hanoi, many healthcare facilities offer basic blood test services. However, selecting a reputable institution with modern equipment and certified laboratories is essential for accurate diagnostics.
At TCI – Thu Cuc Healthcare System, the Laboratory Department is ISO 15189:2012 certified, ensuring international standards in medical testing. Key advantages of undergoing a blood test at TCI include:
– Clinical examination by qualified physicians to identify the appropriate tests needed.
– Automated testing using the Power Express robotic system from the U.S., comparable in quality to labs in Singapore and Japan.
– The system processes up to 1,200 samples per hour, ensuring rapid turnaround.
– Safe and nearly painless sample collection using ultra-fine needles and strict infection control protocols.
– Comprehensive test packages, from basic panels to advanced diagnostics.
With its modern infrastructure and commitment to clinical excellence, Thu Cuc TCI is a trusted destination for residents and expatriates seeking accurate and timely blood test results in Hanoi.