Hyperlipidemia, also known as high blood lipid levels, is a medical condition characterized by an excessive amount of cholesterol and triglycerides in the bloodstream. This condition poses a serious threat to cardiovascular health and significantly increases the risk of severe complications such as stroke and heart attack. Early identification of symptoms, understanding the underlying causes, and timely treatment are essential to prevent complications and maintain long-term health. This article provides comprehensive information on hyperlipidemia to support effective prevention and management.
1. What is Hyperlipidemia?
1.1 Definition
Hyperlipidemia refers to an abnormal increase in lipids (fats) in the blood. These lipids include cholesterol and triglycerides, which are essential for various bodily functions but can be harmful in excess. Elevated lipid levels are one of the leading risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, atherosclerosis, and stroke.
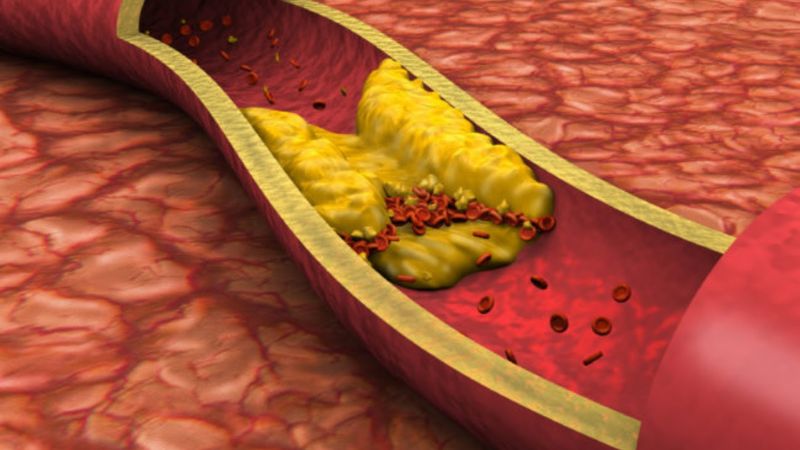
High blood lipids occur when LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, or both are elevated.
1.2 Types of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is generally classified into three main types:
– High cholesterol levels: Excess low-density lipoprotein (LDL or “bad cholesterol”) can lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in arteries.
– High triglyceride levels: Elevated triglycerides may cause acute pancreatitis and increase the risk of heart disease.
– Mixed hyperlipidemia: A combination of high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, further increasing cardiovascular risks.
2. Common Causes of Hyperlipidemia
2.1 Unhealthy Diet
Consuming excessive saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sugar is a major contributor to hyperlipidemia. Frequent intake of fast food, processed foods, and deep-fried items can significantly raise lipid levels.
2.2 Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle reduces the body’s ability to metabolize fats, leading to lipid accumulation in the bloodstream. Regular physical activity is essential to support lipid breakdown and promote overall metabolic health.
2.3 Genetic Factors
Some individuals inherit genetic mutations that affect lipid metabolism. A family history of hyperlipidemia or cardiovascular disease increases the likelihood of developing this condition.
2.4 Underlying Medical Conditions
Diseases such as diabetes, obesity, fatty liver disease, and hypothyroidism can disrupt lipid regulation in the body, leading to elevated blood fat levels.
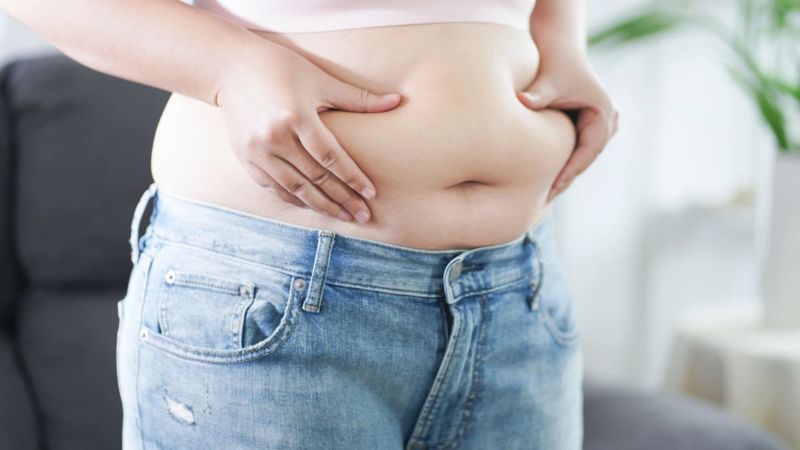

Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for high blood lipids.
3. Recognizing the Symptoms
Hyperlipidemia often progresses silently in its early stages, making routine health check-ups essential. However, some people may experience:
– Headaches, dizziness, or fatigue
– Difficulty concentrating or mild cognitive decline
As the condition worsens, symptoms can become more noticeable:
– Chest pain or tightness
– Numbness or tingling in the limbs
– Visual disturbances or memory impairment
If left untreated, hyperlipidemia can lead to severe complications:
– Atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries)
– Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
– Stroke
– Kidney failure
4. Treatment and Management
4.1 Dietary Changes
Adopting a heart-healthy diet is fundamental. Individuals should limit intake of red meat, animal fats, and processed foods. Instead, focus on foods rich in fiber, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids from sources like salmon, walnuts, and chia seeds.
4.2 Regular Exercise
Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise daily, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or yoga, helps improve lipid metabolism and reduces LDL cholesterol.
4.3 Medications
In more severe cases, doctors may prescribe lipid-lowering medications, such as statins, fibrates, or niacin. It is essential to follow medical instructions carefully to ensure effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.

Early check-ups and treatment can help control high blood lipid levels.
4.4 Managing Related Conditions
Treating comorbidities like diabetes, obesity, or liver disorders is crucial for controlling lipid levels and improving overall health.
5. Preventive Measures
– Healthy Eating Habits: Avoid high-fat and high-sugar foods; choose balanced meals that support cardiovascular health.
– Stay Active: Daily physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also keeps the heart and blood vessels in optimal condition.
– Routine Health Screenings: Regular blood tests, ideally every 6 months for high-risk individuals, help detect lipid abnormalities early. Additional tests may include liver and kidney function, blood glucose levels, carotid ultrasound, or coronary artery imaging.
Hyperlipidemia is a significant health concern that can lead to life-threatening complications if not managed properly. Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following appropriate treatment strategies are vital for protecting your health. Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and scheduling periodic health check-ups are key preventive measures for long-term well-being.








