Hemorrhoids, while often causing discomfort, are typically a benign condition that can be effectively managed. Medications for hemorrhoids are a primary treatment option, particularly in early stages, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
1. Understanding Hemorrhoids and Their Stages
1.1 What Are Hemorrhoids and Why Do They Form?
Hemorrhoids develop from the swelling of veins in the rectal and anal areas due to excess pressure or blood pooling, which eventually leads to the formation of hemorrhoidal tissue. This condition can disrupt daily life, particularly during bowel movements.
Risk factors such as prolonged constipation, a sedentary lifestyle, and physical exertion increase the likelihood of hemorrhoid development. Pregnancy and aging also raise the risk due to added pressure on the veins.
1.2 Stages of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids progress through four stages, ranging from minor to severe, influencing the approach to treatment. Internal hemorrhoids, for instance, start within the anal canal but can protrude externally in later stages. External hemorrhoids form outside the anus, with symptoms that often include pain and swelling.
The progression of hemorrhoids determines whether medications for hemorrhoids will be effective alone or if more intensive treatments, like surgery, are needed.
Hemorrhoids cause considerable inconvenience and discomfort for those affected.
2. Treating Hemorrhoids with Medication: What You Should Know
2.1 When Are Medications for Hemorrhoids Appropriate?
To determine whether medications for hemorrhoids are suitable, a doctor will usually conduct a clinical examination, sometimes using an endoscope, to evaluate the severity. Medications for hemorrhoids are generally recommended for mild to moderate cases (Stages 1 and 2). These treatments include oral medications, topical creams, or a combination of both, based on the symptoms and severity of the hemorrhoids.

Patients need to undergo a medical examination for diagnosis and an appropriate treatment recommendation.
2.2 Types of Medications for Hemorrhoids
Medications for hemorrhoids fall into three main categories: pain and symptom relief, stool softeners, and venotonic drugs (which strengthen veins and improve circulation).
Pain Relief and Symptom Reduction
Pain-relief medications help minimize pain, itching, and inflammation. Options include creams, ointments, and oral pain relievers. Medications for hemorrhoids that focus on pain relief should only be used for limited periods to avoid side effects, and doses should be followed as prescribed.
Stool Softeners
Constipation can exacerbate hemorrhoid symptoms, making bowel movements painful and worsening the condition. Stool softeners, commonly included among medications for hemorrhoids, make bowel movements easier, reducing strain and discomfort. Patients are advised to stay hydrated and consume high-fiber foods to support stool softening effects.
Venotonic Drugs
Venotonic drugs enhance vein elasticity, preventing hemorrhoids from becoming further enlarged. These medications are often prescribed for patients with weak vein walls or circulatory issues. If these drugs are ineffective, a doctor may recommend other treatment options.
2.3 What to Do If Medications Are Ineffective
If hemorrhoids advance beyond mild stages, medications may not provide sufficient relief. In such cases, surgical interventions are often suggested. Options include Diode Laser therapy, which is minimally invasive, Longo surgery for hemorrhoids, and other advanced methods that minimize recovery time.
Thu Cuc TCI offers a range of hemorrhoid treatments, including the highly effective Diode Laser therapy, which allows for fast recovery and minimal pain.
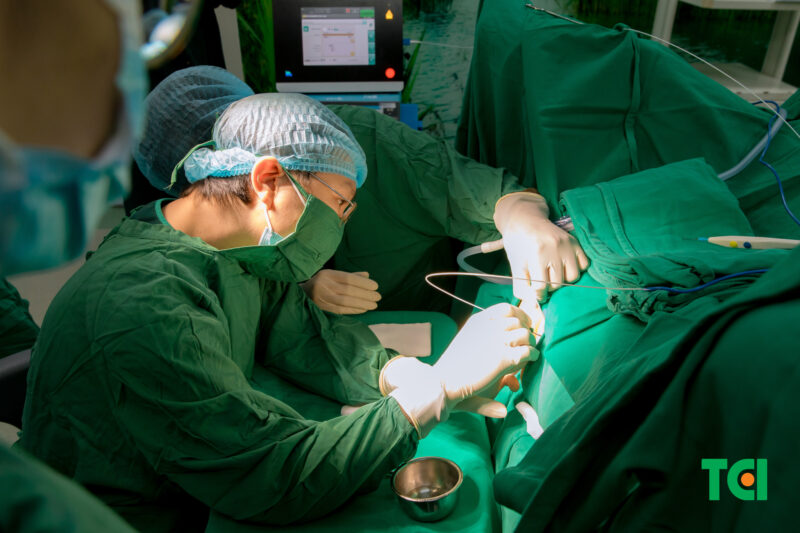
Treating advanced hemorrhoids with the diode laser method.
If you experience hemorrhoid symptoms, consult a healthcare professional to discuss your condition and the best treatment approach.








