High-resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) is a cutting-edge technique utilized to investigate esophageal motility disorders and dysfunctions. Recognized as the gold standard in diagnosing esophageal motility disorders, HRM employs specialized pressure sensors to measure the pressure within the esophagus, providing crucial insights into whether the esophagus is functioning properly.
1. Role of High-Resolution Esophageal Manometry
High-resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) is pivotal in assessing esophageal motility and verifying the normal functioning of the esophagus. By using precise pressure sensors, HRM can determine the presence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and offer differential diagnoses for conditions related to swallowing difficulties and sensations of obstruction. This technology enables physicians to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Symptoms such as belching, heartburn, and difficulty swallowing can arise from various causes, not just GERD. In many cases, patients treated for GERD may not have the condition as the root cause of their symptoms. HRM plays a critical role in such scenarios by thoroughly exploring esophageal motility and functionality, thereby guiding accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatments.
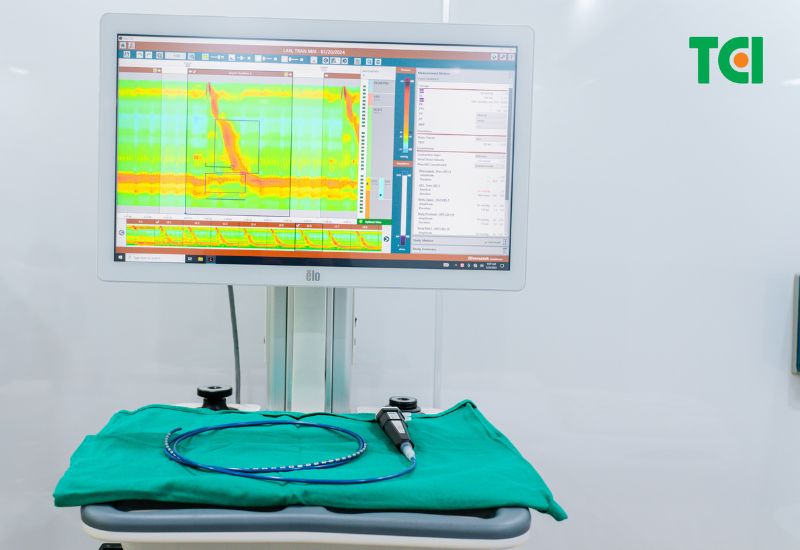

Image of the high-resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) device.
2. Indications for HRM
2.1. When to Perform HRM
HRM is essential in various clinical scenarios, including:
– Unexplained difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, a sensation of food sticking in the throat, or choking.
– Persistent heartburn and acid regurgitation.
– Unexplained chest pain, after excluding cardiovascular causes.
– Suspected esophageal motility disorders such as achalasia, Jackhammer esophagus, or diffuse esophageal spasm.
– Patients exhibiting GERD symptoms unresponsive to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy.
– Systemic diseases (e.g., scleroderma) presenting with esophageal symptoms.
– Determining the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) location for esophageal pH monitoring.
– Pre- and post-surgical evaluations of the LES function.
2.2. Contraindications
HRM is contraindicated in patients with severe cardiovascular or respiratory diseases, those allergic to the materials used in the device, and patients with esophageal obstructions due to surgeries, suspected or confirmed esophageal cancer, strictures, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, or nasal and throat conditions. Pregnant women and patients with mental health conditions that prevent cooperation during the procedure are also excluded.
Patients undergo examinations and follow doctor’s instructions.
3. High-Resolution Esophageal Manometry (HRM) Procedure
3.1. Pre-Procedure Requirements
Patients must adhere to the following guidelines before undergoing HRM:
– Fast for at least 6 hours before the procedure.
– Avoid calcium channel blockers or smooth muscle relaxants for 24 hours prior to the procedure.
– Ensure complete recovery from any sedative effects if an endoscopic examination was performed prior.
– Confirm that no contraindications apply.
3.2. HRM Procedure Steps
TCI – Thu Cuc Healthcare System follows a structured HRM procedure:
Patient Reception:
– Initial consultation with a physician to determine the need for HRM.
– Preparation of HRM documentation by nursing staff.
Procedure Execution:
– Patient preparation, including nasal anesthetic application and throat spray, followed by rest.
– Insertion of the catheter by the technician, with the patient following specific instructions for necessary movements.
– Catheter removal and result analysis, taking approximately 20 minutes.
Post-Procedure:
– The patient consumes a light meal and rests.
– Result interpretation by the physician in the initial consultation room.
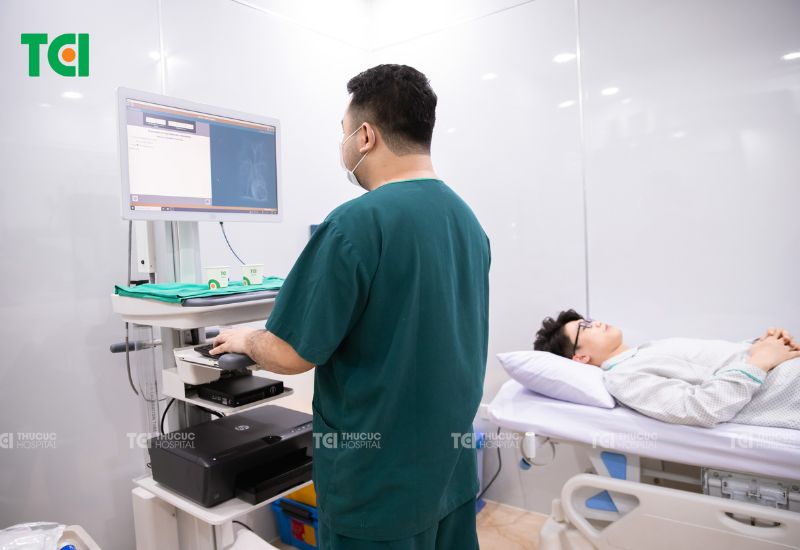
Conducting high-resolution esophageal manometry at TCI
4. Common Questions about High-Resolution Esophageal Manometry (HRM)
4.1. Is HRM Painful? Is Anesthesia Required?
HRM may cause slight discomfort during catheter insertion, but this is minimal with patient cooperation. Throat anesthetic spray is used; general anesthesia is not necessary as patient alertness is required for swallowing and other actions during the procedure.
4.2. Duration of HRM
The entire HRM process takes about 20-30 minutes.
4.3. Post-HRM Recovery and Side Effects
Patients typically experience no significant side effects and do not require hospitalization post-HRM. Minor side effects like nasal bleeding, throat discomfort, or mild swelling may occur but are generally insignificant. Medical staff monitor vital signs such as blood pressure, pulse, and respiration throughout the procedure to ensure patient safety.
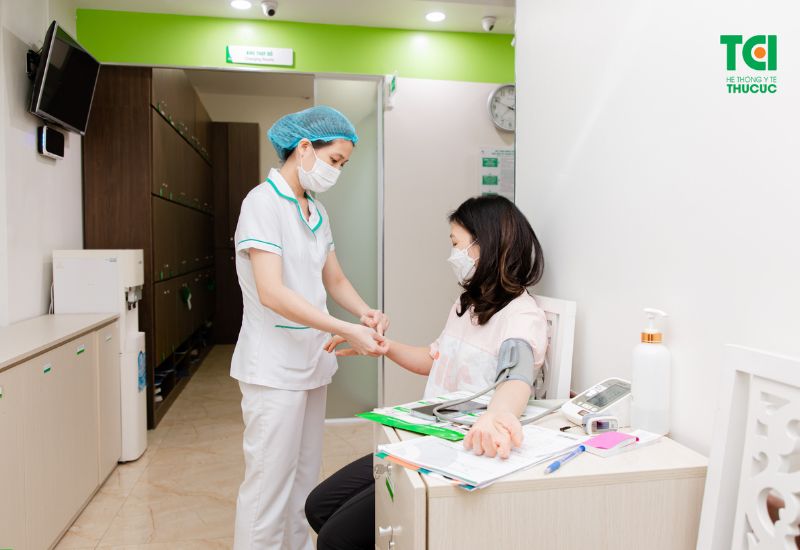
Patients have their blood pressure checked for safety after HRM
High-resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) stands as the most advanced method for diagnosing esophageal motility disorders, offering unparalleled diagnostic accuracy. For individuals experiencing gastrointestinal or esophageal issues, contacting TCI Healthcare System for consultation and scheduling an HRM can provide the necessary diagnostic clarity and guide effective treatment plans.








