Handling foreign object choking in children requires careful attention, proper assessment of the situation, and accurate, appropriate actions to protect the child’s health and life. Parents should be aware of the following information and work with healthcare providers like TCI to prevent choking incidents and protect their children from the dangers associated with such situations.
1. Understanding Foreign Object Choking in Children
Foreign object choking occurs when a child swallows an item that cannot easily pass through the airway or digestive tract. These objects can range from food and small toys to other household items. According to TCI medical experts, prompt treatment is crucial, especially in children, as foreign object choking can lead to severe consequences, including death.
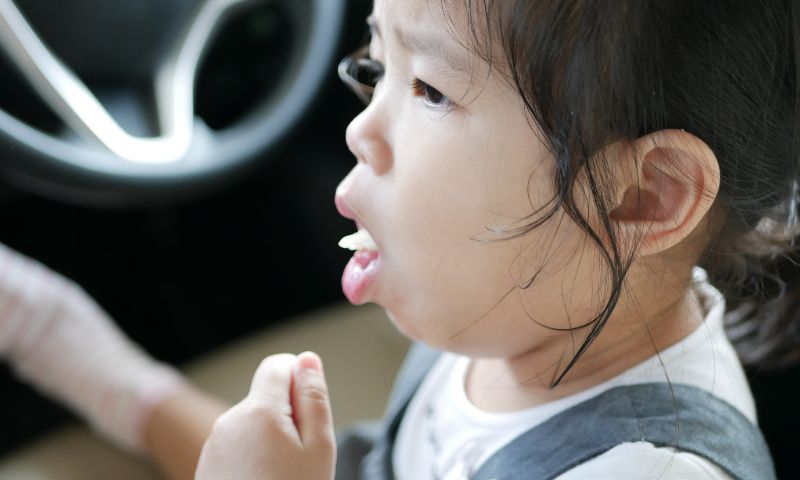

A child choking on a foreign object
1.1 Causes
Children are particularly vulnerable to choking on foreign objects due to several factors:
– They often put small objects in their mouths out of curiosity or habit without understanding the dangers.
– Food that is not properly chewed or cut into small pieces increases the risk.
– Distractions like watching television, playing with phones, or talking while eating can lead to accidental choking.
– Some children may have swallowing difficulties due to underlying medical conditions or congenital abnormalities.
1.2 Signs of Choking
Parents should be alert to the following signs that may indicate their child is choking:
– Sudden crying
– Difficulty swallowing or feeling of something stuck
– Gagging or retching
– Severe coughing, sometimes accompanied by wheezing
– Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
– Trouble speaking or loss of voice
– Pale or bluish skin tone
– Loss of consciousness
The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the child’s age, the size and shape of the object, and its location.
1.3 Risks of Improper Handling
In cases where the foreign object is small and non-severe, the child may be able to expel it naturally through coughing. However, young children are often too frightened and may not know how to handle the situation effectively. This can lead to the object becoming lodged deeper, making it difficult for the child to clear the airway on their own. In such cases, prompt medical intervention is essential to remove the object using specialized tools. This should be performed by experienced ENT specialists to avoid complications such as:
– Infection: A foreign object lodged in the airway can create an environment for bacteria to grow, leading to respiratory infections, which can cause coughing, fever, and difficulty breathing.
– Airway Damage: Attempting to remove the object manually or with inappropriate tools can injure the airway, causing bleeding, swelling, and potentially making breathing more difficult.
– Lung Complications: If not removed promptly, the object could move into the lungs, leading to complications such as pneumonia, lung abscess, or pneumothorax (collapsed lung), which are life-threatening and require urgent medical care.
– Complete Airway Obstruction: The object could fully block the airway, leading to suffocation and death within minutes.
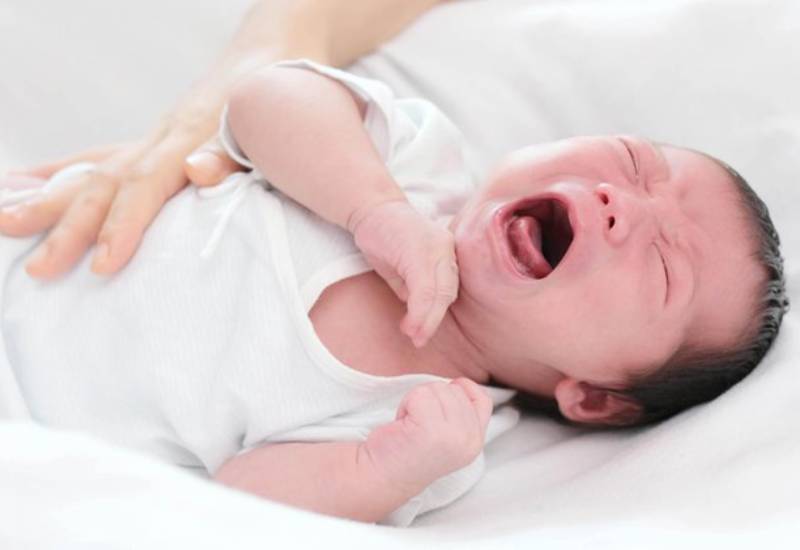

If not promptly addressed, a child choking on a foreign object can lead to serious dangers
2. Emergency Management of Foreign Object Choking in Children
Choking due to a foreign object in children is a medical emergency that requires immediate action. When a child shows severe symptoms, it is crucial to call emergency services while performing first aid. For manageable cases, careful consideration is needed to select the appropriate response.
2.1 Initial Assessment and Response
Quickly assess the child’s breathing:
– If the child can breathe normally, encourage them to cough forcefully to expel the object.
– If the child can cough but is struggling to breathe, perform back blows or abdominal thrusts.
– If the child cannot breathe or cough, call emergency services immediately and begin CPR if necessary.
– If the child is old enough to communicate, ask them about the object they swallowed, as this information can guide medical treatment.
2.2 First Aid Procedures
Back Blows:
– Use the heel of your hand to deliver five firm back blows between the child’s shoulder blades.
– Repeat until the object is dislodged or the child begins to cough strongly.
Abdominal Thrusts (Heimlich Maneuver):
– For children over one year old: Stand or kneel behind the child, wrap your arms around their waist, and place a fist just below the rib cage. Grasp your fist with the other hand and give five quick, upward thrusts. Repeat as necessary until the object is expelled.
– For infants under one year old: Lay the infant face down on your forearm with the head lower than the body. Deliver five firm back blows between the shoulder blades. If the object is not expelled, turn the infant over and perform chest compressions with two fingers on the breastbone.
Important Note: Avoid using your fingers to remove the object from the child’s throat, as this may push it further in or cause additional injury. If unsure about how to perform these procedures, call for emergency assistance immediately.
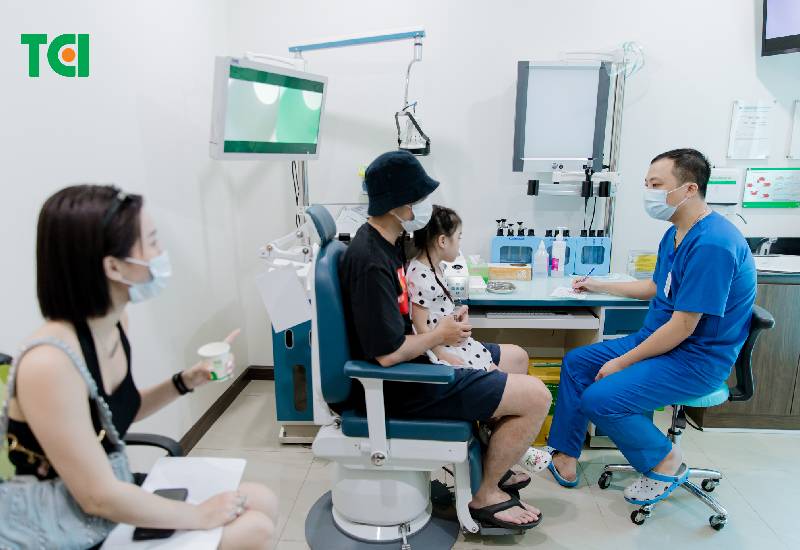
A child choking on a foreign object should see a doctor and receive proper treatment
2.3 Post-First Aid Care
After administering first aid, continue monitoring the child:
– Ensure that the child is breathing normally.
– If the child shows any signs of breathing difficulty, seek immediate medical attention.
– Document important details, such as the type of object, time, and location of the incident, and the actions taken. This information can be vital for healthcare providers in subsequent treatment.
– Take preventive measures to protect your child in the future, such as supervising play with small objects, cutting food into small pieces, and ensuring that children are not distracted while eating.
In summary, quick and appropriate action is essential when managing foreign object choking in children. Delay or improper handling of the situation can have serious health implications, including life-threatening consequences. Even in less severe cases, it is crucial to seek medical attention to ensure the child’s safety and prevent future incidents.








