Peptic ulcers are a common gastrointestinal condition that can be effectively treated if detected early. However, delayed treatment can lead to severe complications. This article provides comprehensive information about peptic ulcers, including symptoms, stages, complications, causes, preventive measures and treatment of peptic ulcers.
1. What are Peptic Ulcers?
Peptic ulcers are lesions in the stomach lining, causing inflammation and sores. In the early stages, small ulcers may heal on their own. However, larger ulcers causing significant symptoms require medical intervention to determine the most effective treatment plan.
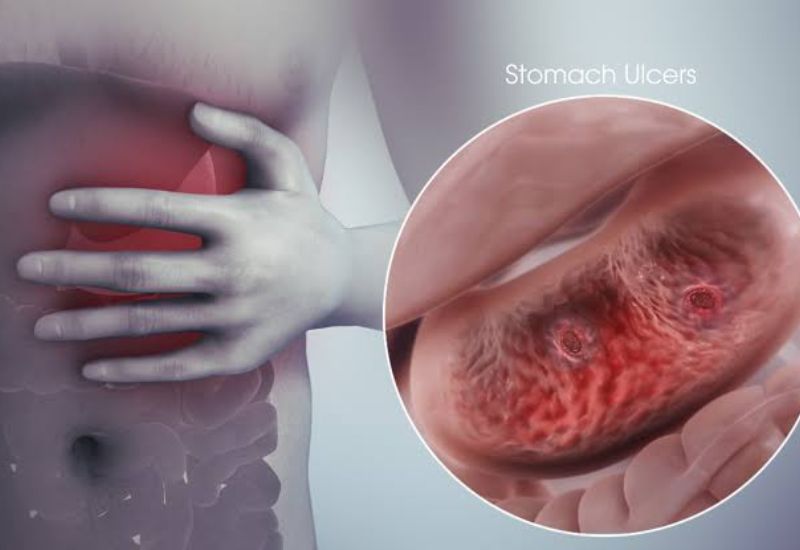
Peptic ulcers occur when the stomach lining is damaged, causing inflammation and sores.
2. Common Symptoms of Peptic Ulcers
Early detection of peptic ulcers can be challenging due to subtle symptoms. Be mindful of the following changes in your body to recognize potential signs of peptic ulcers:
– Abdominal pain and indigestion
– Nausea
– Belching and acid reflux
– Burning sensation in the upper abdomen
– Persistent or intermittent pain
– Digestive issues causing constipation or diarrhea
– Insomnia due to bloating or nighttime abdominal pain
– Physical weakness
– Unintentional weight loss
– Loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting after eating
– Black stools
3. Stages of Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers progress through two main stages:
– Acute Ulcers: Symptoms appear briefly and can be cured with prompt and appropriate treatment. However, patients often neglect early medical consultation.
– Chronic Ulcers: Long-term inflammation leads to chronic ulcers, which are harder to treat and may cause complications like atrophic gastritis, pyloric stenosis, gastrointestinal bleeding, gastric cancer, and infection spread to nearby organs.

Peptic ulcers are divided into two stages: acute and chronic.
4. Complications of Peptic Ulcers
Untreated peptic ulcers can result in serious complications:
– Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Causes anemia, dizziness, pale skin, vomiting blood, or black stools.
– Gastric Perforation: Leads to severe epigastric pain and a rigid abdomen.
– Pyloric Stenosis: Causes rapid weight loss and vomiting due to obstructed food passage in the digestive system.
– Gastric Cancer: Chronic ulcers may develop into malignant tumors in the stomach.
5. Causes of Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers are primarily caused by:
– Helicobacter pylori Infection: This bacterium invades the stomach lining, releasing toxins that damage the mucosal barrier, forming ulcers.
– Long-term Use of NSAIDs: Prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can harm the stomach lining by inhibiting protective mechanisms.
Other less common causes include:
– Excessive Gastric Acid Secretion: Factors like genetics, smoking, stress, and certain foods can increase acid production.
– Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: A condition causing excessive acid secretion in the stomach.
6. What to Do if You Have Peptic Ulcer Symptoms
If you notice symptoms of peptic ulcers, seek early medical consultation for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
6.1 Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcers
– Clinical Examination: Your doctor will inquire about your symptoms, duration, and medications you are using or have used.
– Laboratory Tests: Blood tests for Helicobacter pylori antibodies, stool tests, and breath tests.
– Gastroscopy: This standard procedure allows doctors to visually inspect the stomach lining, accurately assess ulcer severity, and perform biopsies to check for infections or other issues.
6.2 Treatment of Peptic Ulcers
Treatment plans vary based on the ulcer’s severity and cause. Common treatment methods include:
– Medical Treatment: Doctors prescribe medications to effectively manage symptoms. Patients should adhere strictly to the prescribed dosage and duration to avoid drug resistance.
– Surgical Treatment: Surgery is necessary if medications fail, ulcers do not heal, or complications like bleeding, perforation, or pyloric stenosis arise.
7. Preventing Recurrence of Peptic Ulcers
Effective prevention methods include:
– Healthy Eating Habits: Avoid alcohol, tobacco, spicy and acidic foods. Eat regular meals, avoid overeating or fasting, and avoid late-night meals. Include fruits, vegetables, and foods rich in vitamin C and zinc. Ensure food is well-cooked and practice good hand hygiene.
– Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Quit smoking and avoid alcohol and caffeine-containing drinks.
– Consult a Doctor: Seek medical advice if symptoms persist.
– Manage Stress: Stay positive and manage stress through activities like yoga, meditation, music, or reading. Stress can exacerbate ulcer symptoms.

Follow a healthy and balanced diet to prevent the recurrence of peptic ulcers.
This comprehensive guide provides essential information on peptic ulcers, helping you to manage and prevent the condition effectively. The treatment of peptic ulcers should always be approached with a comprehensive plan to ensure full recovery and prevent recurrence. Effective treatment of peptic ulcers involves adhering to medical advice, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-ups. Early diagnosis and consistent treatment of peptic ulcers are crucial in managing this condition and avoiding severe complications. Seek early medical consultation if you experience any symptoms for prompt and thorough treatment.








