Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose (sugar) levels due to defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both. Left untreated or poorly managed, diabetes can lead to serious complications affecting multiple organ systems. Notably, this chronic metabolic disorder is becoming increasingly common among younger individuals, making early recognition and prevention all the more critical.
1. Common Types of Diabetes and Their Symptoms
Diabetes is generally classified into three main types: Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Each type presents with different clinical signs and symptoms:
1.1 Type 1 Diabetes
This form of diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, insulin production is either absent or severely reduced. Key symptoms include:
– Increased hunger and fatigue: Since glucose cannot be absorbed into the cells for energy due to lack of insulin, the body experiences fatigue and persistent hunger.
– Frequent urination and excessive thirst: High blood glucose levels disrupt kidney function, leading to increased urination and subsequent dehydration, which triggers thirst.
– Dry mouth, itchy or dry skin: Fluid loss from frequent urination results in dry mucous membranes and skin discomfort.
– Unexplained weight loss: Despite eating more, individuals may lose weight rapidly as the body breaks down fat for energy in the absence of glucose utilization.
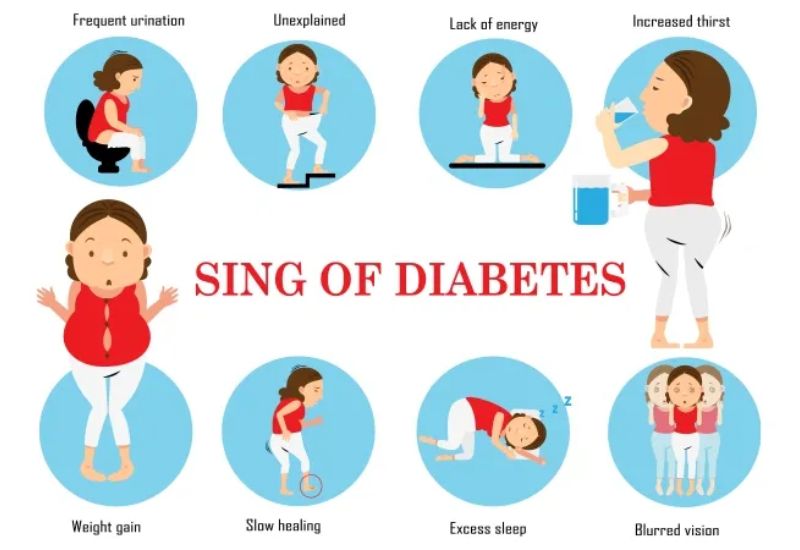
Common symptoms of blood sugar
1.2 Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin over time. Unlike type 1, this type progresses slowly and symptoms may go unnoticed for years. Common indicators include:
– Yeast infections: Elevated blood sugar creates a favorable environment for fungal growth, particularly in moist areas like under the breasts, between fingers and toes, or around the genitals.
– Slow-healing wounds: Persistently high glucose levels damage blood vessels and nerves, impairing circulation and slowing down the healing process.
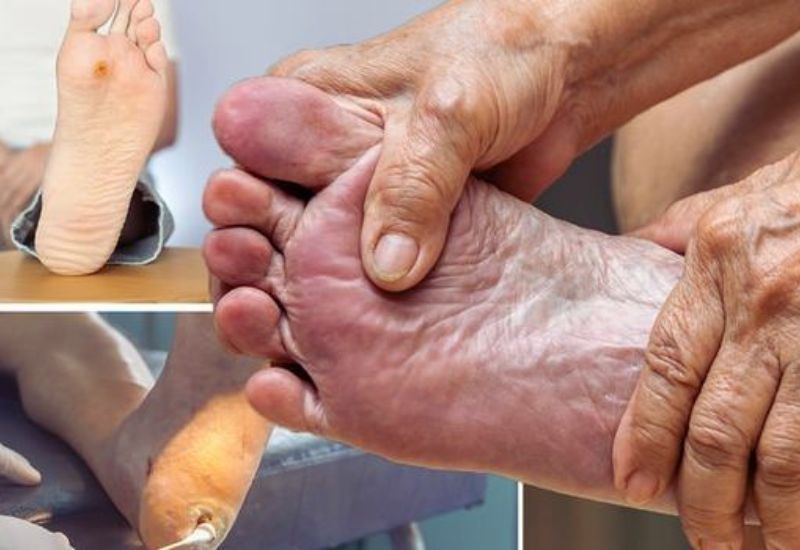
Signs of type 2 diabetes
1.3 Gestational Diabetes
This type occurs during pregnancy and is often asymptomatic. Expectant mothers may notice increased thirst or urination, but diagnosis typically relies on routine glucose tolerance testing performed around the 28th week of pregnancy.
2. Diabetes Treatment
Effective diabetes management involves a multidisciplinary approach and begins with a diagnosis by an endocrinology specialist. While there is currently no definitive cure for this chronic metabolic disorder, the disease can be effectively controlled.
– Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy.
– Type 2 diabetes may initially be managed with lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthier diet and increasing physical activity. If lifestyle interventions are insufficient, oral medications or injectable insulin may be prescribed to help regulate blood glucose levels.
Patients should adhere strictly to the treatment plan outlined by their physician and attend regular follow-ups. Medical professionals will also provide personalized recommendations on nutrition, exercise, and daily habits to optimize disease control.

Prompt and accurate diagnosis is needed if symptoms are detected
3. Preventing Diabetes
While type 1 diabetes is largely associated with genetic and autoimmune factors and is difficult to prevent, type 2 chronic metabolic disorder can often be delayed or avoided through healthy lifestyle choices. Preventive strategies include:
– Maintaining a balanced diet: Limit intake of sugary foods and beverages, processed meals, and trans fats. Focus on consuming whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
– Regular physical activity: Engage in consistent, moderate-intensity exercise such as walking, cycling, or swimming.
– Monitoring health proactively: Individuals with a family history of this chronic metabolic disorder should be especially vigilant. Routine health check-ups and blood sugar testing can aid in early detection and prompt intervention.
Understanding the signs, treatment, and prevention of chronic metabolic disorder is crucial to managing the disease and maintaining a good quality of life. Although chronic metabolic disorder remains incurable, it is a manageable condition. With timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with this chronic metabolic disorder can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. If you notice symptoms or are at risk, consult a trusted medical facility for proper evaluation and support.








